Material Graphs
Material Graphs define the look of a material and must contain (for now) a single Material Node.
For example, this is a simple Material Graph. The graph connects a constant color value to a Material Node's emissive field:
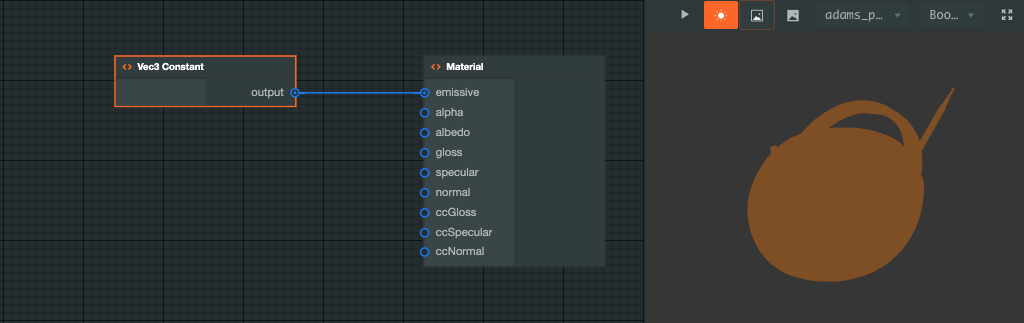
As can be seen above, the Material Node has a number of input ports. Each port controls an aspect of the runtime lighting environment. The port details are as follows:
| Port | Type | Default | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| emissive | RGB | (0, 0, 0) | Color is added directly to the other lighting components of the material. |
| alpha | Number | 1 | The surface opacity. |
| albedo | RGB | (0, 0, 0) | The surface diffuse color. |
| gloss | Number | 0? | The smoothness / roughness of the surface. |
| specular | RGB | (0, 0, 0) | Tints the specular color. |
| normal | XYZ | (0, 0, 1) | The surface normal. |
| ccGloss | Number | 0? | Clear coat gloss. |
| ccSpecular | RGB | (0, 0, 0) | Clear coat specular. |
| ccNormal | XYZ | (0, 0, 1) | Clear coat normal. |